Source: The Conversation (Au and NZ) – By Jeff Borland, Professor of Economics, University of Melbourne
Incentives, the Freakonomics author Steven Levitt once quipped, are the “cornerstone of modern life”. To this I would add: only if the incentive is big enough.
In Australia at present there is considerable support for increasing the JobSeeker unemployment payment by a significant amount to make up for decades in which it has fallen relative to wages and other payments.
Opponents say an increase might adversely affect incentives to search for and take up paid work.
I have reviewed this claim in recent research and find even a substantial increase in JobSeeker wouldn’t be big enough to make a difference.
If JobSeeker was to climb A$125 per week from $282.85 to $407.85, it would still be only a little more than half the national minimum wage.The increase would leave JobSeeker recipients at the very bottom of the distribution of earnings of full-time adult workers – the bottom percentile. This means 99 out of every 100 full-time jobs would pay more.
Read more: Top economists want JobSeeker boosted by $100+ per week and tied to wages
A higher JobSeeker payment of $125 per week could also preserve a significant financial incentive for recipients to take on extra days of paid work.
Under the current income test, the marginal gain from working an extra day at the minimum wage would range from $93 (for the first day) to $34 (third day).
Under a better income test the gain could be smoothed across the week.
The real-life experiment
We have just had a real-life experiment that has told us what happens to incentives to shift into paid work when JobSeeker is nearly doubled.
The payment was almost doubled between March and September 2020, being boosted by a coronavirus supplement of $275 per week.
JobSeeker vs age pension
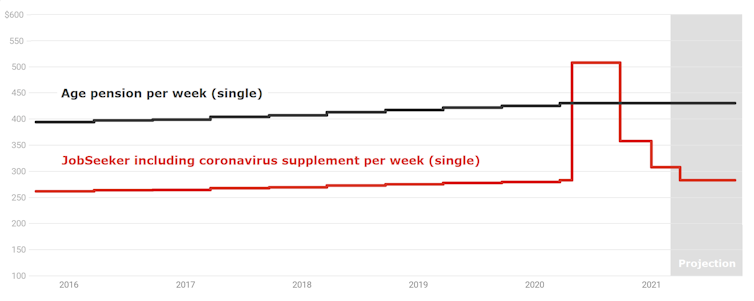
If getting the doubled payment meaningfully reduced incentives to take up paid work, JobSeeker recipients would be less likely to move from unemployment into employment than before, and job vacancies would take longer to fill.
Neither happened while JobSeeker was doubled.
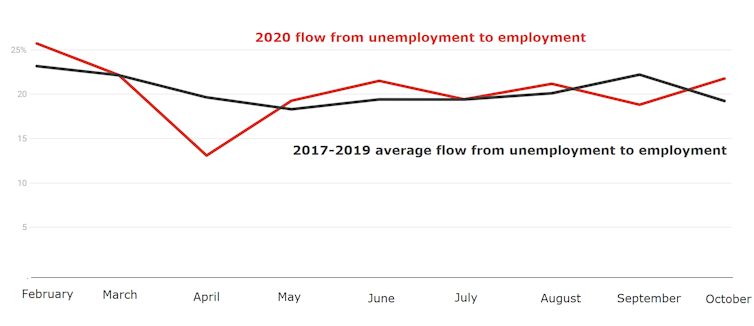
Compared to the previous years of 2017, 2018 and 2019 the flow from unemployment into employment collapsed in April when the onset of COVID-19 cost 607,000 people their jobs.
But in the following months, while JobSeeker remained doubled, the proportion of unemployed people who transitioned into employment returned to previous monthly benchmarks.
Flows from unemployment to employment
Second, there is no evidence of a rise in the vacancy rate, as would be expected if the increased JobSeeker payment was having a major impact on incentives to work.
The vacancy rate fell between February and April as would be expected, and then regained some losses, but at no point climbed higher than before the collapse, even with higher JobSeeker payments.
More JobSeeker might help
Searching for jobs takes time and costs money. More income from JobSeeker means less financial stress and more “bandwidth” to commit to job search, and more resources such as the ability to pay for transport to and clothing for interviews.
Read more: ‘If JobSeeker was cut, the unemployed would be picking fruit’? Why that’s not true
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development made this point a decade ago in its review of Australia.
It said Newstart (the old name for JobSeeker) had fallen to the point where questions could be asked about its “effectiveness in providing sufficient support for those experiencing a job loss, or enabling someone to look for a suitable job.”
– ref. New finding: boosting JobSeeker wouldn’t keep Australians away from paid work – https://theconversation.com/new-finding-boosting-jobseeker-wouldnt-keep-australians-away-from-paid-work-150454




