Source: The Conversation (Au and NZ) – By Steve Turton, Adjunct Professor of Environmental Geography, CQUniversity Australia

Millions of people in southeastern Australia are sweating through a record-breaking heatwave. The heat this week is likely to be one for the history books. The heat began on Saturday January 24th. On Australia Day, three sites in South Australia and two in New South Wales broke their all-time temperature records. Ceduna reached a whopping 49.5°C in the shade – just 1.2°C off the highest temperature ever recorded in Australia.
Today, temperatures have topped 49°C in northwest Victoria and South Australia for the first time on record, and many towns face days of heat over 40°C. Regions such as the Otway Ranges in Victoria are facing extreme fire danger. Renmark in South Australia has reached 49.3°C and Walpeup in Victoria has reached 48.7°C.
This is shaping up as the worst heatwave since the Black Summer of 2019-20. The intense heat that summer contributed to catastrophic bushfires which burnt 21% of the continent, an area still considered globally unprecedented.
Independent analysis found the last heatwave between January 5 to 10 was made over five times more likely by global heating. This current heatwave is substantially worse, but we’ll have to wait for attribution studies to understand how much global heating has contributed to its overall severity.
The sustained heat hitting the southeast will be widespread and prolonged. It’s likely more all-time temperature records will be broken this week, as the body of hot air stagnates over the south and southeast. People in exposed areas should heed warnings from the Bureau of Meteorology and advice from health and emergency response authorities.
What’s driving this heatwave?
The Pilbara region in northwest Western Australia is sometimes called the nation’s “heat engine”. This large, sparsely populated area is very dry. When heat hits Pilbara rocks and sands, it can quickly build up. Weather conditions are very stable, and Pilbara heatwaves can last weeks.
But that doesn’t explain how the heat gets to population centres in Australia’s south and southeast.
Over summer, there are often active monsoonal troughs (areas of low atmospheric pressure) over northern Australia. As the monsoon brings heavy rain and low pressure systems to parts of northern Australia, it pushes high pressure systems, known as heat domes, further south. This directs intense heat thousands of kilometres towards the southern, central and eastern parts of the continent.
Tropical monsoonal low-pressure systems in the north often work in tandem with slow-moving high pressure systems in the Tasman Sea or Great Australian Bight. The result is a weather pattern able to shift hot air masses thousands of kilometres to reach the southern states.
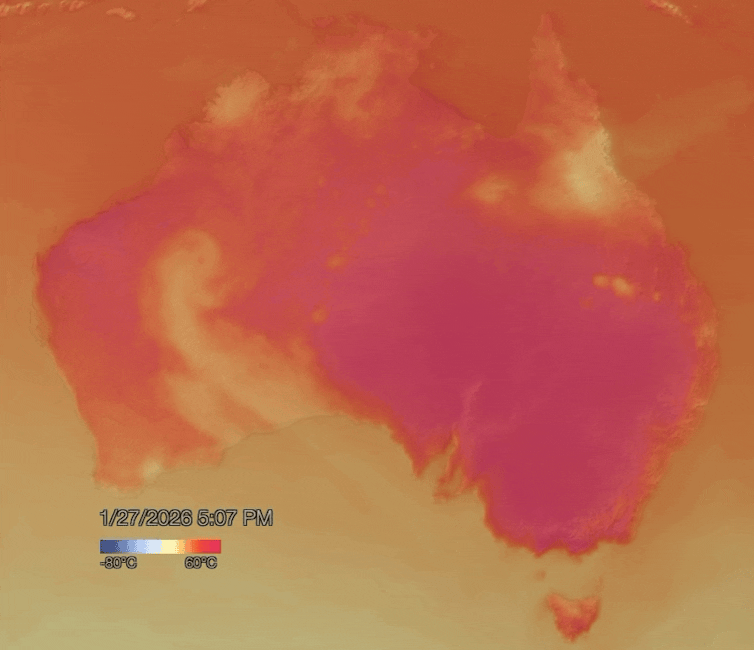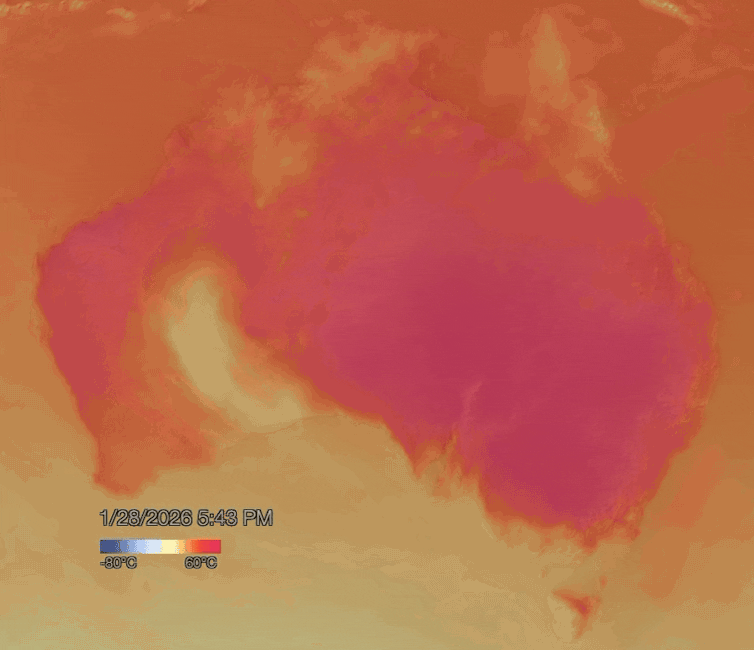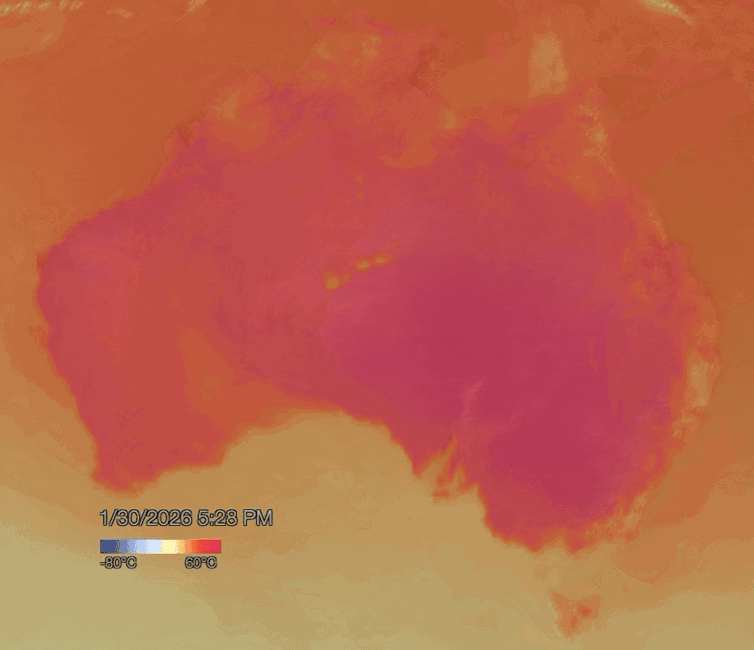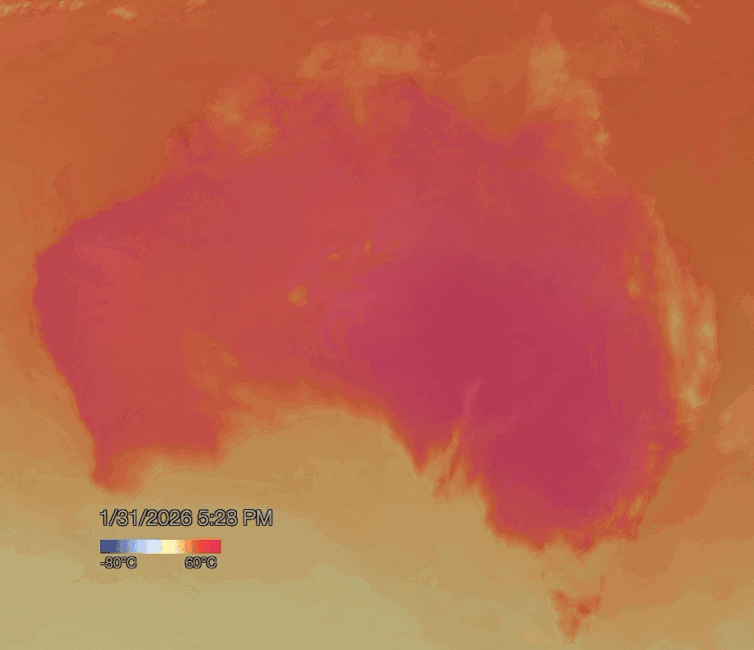
NOAA Visualisation Lab
Blocking highs are strong high pressure systems which can sit in place for days or even weeks, blocking other weather systems from moving in. The blocking high pressure system responsible for the current heatwave is staying put in the atmosphere a few kilometres above New South Wales.
As winds blow from areas of high pressure to low pressure in the atmosphere, air is forced to flow down towards the surface. As the air descends, it compresses due to rising atmospheric pressure. Compression heats the air further, which can make heatwaves hotter and longer-lasting.
When conditions like this are in place, hot northerly winds often persist for days, funnelling more and more desert heat towards the coasts. This can cause temperatures to exceed 40°C in states such as South Australia, Victoria, New South Wales and southern Queensland.
During this extreme heatwave, maximum temperatures in some southern towns are approaching 50°C – the sort of temperature once restricted to famously hot towns such as Marble Bar in Western Australia.
The official Australian record for the maximum temperature in the shade is 50.7°C, recorded at Oodnadatta (South Australia) in 1960 and Onslow (Western Australia) in 2022. This shared all-time record may be broken at several southeast inland locations this week as atmospheric conditions are amplified by the steady drumbeat of global heating.
During severe, prolonged heatwaves, intense daytime heat is accompanied by hot nights. The humidity can sometimes also increase due to tropical moisture being transported south. The combination of heat and humidity (measured as heat indices) is particularly dangerous to humans, livestock and wildlife.
Should this heatwave be named?
For decades, tropical cyclones hitting Australia have been given names. Should heatwaves similarly be given names to encourage people to take them seriously? Names can make weather hazards more memorable, helping people recall warnings, share information with neighbours and prepare more effectively.
This week’s heatwave would be an excellent candidate for naming. It is severe, breaking all-time records, long-lasting and widespread. It is also threatening major metropolitan centres with high populations, as well as major regional centres and nationally important agricultural districts. To date, there’s no sign authorities plan to name it.
Responding to future heatwaves
Climate scientists now widely agree average global temperatures will permanently rise 1.5°C over pre-industrial levels by the early 2030s. They may reach 2.7°C by the 2090s if global carbon emissions do not fall sharply.
This means future heatwaves are likely to strike more often and hit harder when they arrive.
We need to adapt to the increasing threats posed by more and worse heatwaves even as we work to cut emissions. Extreme heat is a public health issue, to say nothing of the threats it poses to our wildlife and livestock who have no escape.
![]()
Steve Turton has previously received funding from the Australian and Queensland governments.
– ref. Where did southern Australia’s record-breaking heatwave come from? – https://theconversation.com/where-did-southern-australias-record-breaking-heatwave-come-from-274417





