Source: The Conversation (Au and NZ) – By Oliver A.H. Jones, Professor of Chemistry, RMIT University

If not the root of all evil, chemical pollution is surely responsible for a good chunk of it. At least, that’s how it feels sometimes when reading the news and the latest research.
From hormone disruptors in our rivers and drugs in our drinking water, to PFAS and microplastics just about everywhere, it seems there’s plenty to worry about.
The list of potential health effects is also scary. Pollution is linked to infertility, cancer, reduced immune function, and more.
So it’s not surprising many people feel chemicals are intrinsically bad, though that’s not the case. But how worried should we really be, and can we reduce the risks?
In the air we breathe
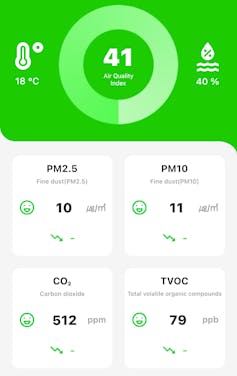
Globally, pollution is a serious problem – particularly air pollution.
Oliver Jones
The Lancet Commission on pollution and health estimates pollution is responsible for about 9 million deaths a year and economic losses in the trillions of dollars.
The burden of disease falls heavily on developing countries, but even in Australia air pollution causes significant harm.
Fortunately, we can monitor air pollution, even at home. We know what levels are dangerous, and how to reduce exposure. But what about things we can’t monitor, or know less about?
The water we drink
In June, the Sydney Morning Herald implied tap water throughout Australia was contaminated with alarming levels of PFAS. But the levels detected fall within Australia’s drinking water guidelines. They just happen to exceed the United States’ new safety thresholds, which don’t come in for five years.
Oliver Jones
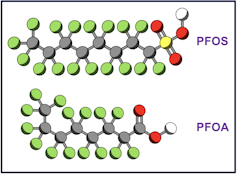
PFAS (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a group of highly persistent chemicals characterised by carbon-fluorine bonds.
Although PFAS in your water sounds awful, we don’t know if water is the main route of exposure or what the actual risks are.
PFAS is also in dust, cookware, waterproof clothing, cosmetics, and other consumer products.
The presence of PFAS is an emotive subject, thanks to films such as Dark Waters and documentaries like How to Poison a Planet.
Found everywhere from Mount Everest to the ocean depths, PFAS have been associated with negative health effects including cancer and reduced immune response.
What is generally missing from both research papers and news reports is context – details on the dose and duration of exposure needed to cause such effects.
The levels of PFAS needed to cause health effects tend to be orders of magnitude higher than those typically found in the environment. So while it’s not great that we’ve polluted the entire planet with these compounds, the health risks for most of us are likely to be low.
New technologies are being developed to reduce PFAS in water and soil.
But given their widespread distribution and extreme persistence, we should perhaps reevaluate PFAS risks and regulations (as the National Health and Medical Research Council is doing).
If you want to reduce your exposure, you can consider using water filters and avoid non-stick pans and other products that contain PFAS.
Many non-stick pans now boast they are PFAS-free. Sadly this is not always the case. Ceramic pans can be a good, PFAS-free option, but these are actually silica-based and may not last as long.
And the food we eat
Everyone knows pesticides give you cancer right? Well, actually no. This is another area where public perception has jumped ahead of the science.

Oliver Jones
The usual suspect, glyphosate, is usually claimed to cause non-Hodgkin lymphoma. But this is a catch-all term covering more than 60 different types of lymphoma, which can vary significantly.
Multiple independent regulatory agencies worldwide list glyphosate as non-carcinogenic. A study of more than 54,000 people who applied pesticides for a living found no link to cancer.
Small amounts of pesticide residue are permitted on our food, but concentrations are in the parts per trillion (for reference, a trillion seconds is 31,710 years).
The evidence suggests parts per trillion of pesticides do not increase the risk of cancer in people. But if you want to reduce your exposure anyway, washing and cooking vegetables and washing fruit is a good way to go.
Microplastics are everywhere
Microplastics (plastic particles less than 5mm in diameter) are now found everywhere from the top to the bottom of the planet.
They have been reported in food and drink, including salt, seafood, various meats and plant-based proteins, fruit and vegetables as well as bottled and tap water.
Again, it sounds scary – but several reports of microplastics in food and blood have been firmly criticised by other scientists. The widely (mis)reported claim that we eat a credit card’s worth of microplastic each week was debunked by YouTuber Hank Green.
The World Health Organization recently concluded evidence of the health effects of microplastics is insufficient. However, they also make the point that this is not the same as saying microplastics are safe. We need more data to understand the risks.
Avoiding plastic bottles and food packaging can reduce exposure, as can having hard floors rather than carpets, and regular vacuuming.
We need new recycling technology to reduce plastic waste. Ultimately, we may need to wean ourselves off plastic entirely.
Where to from here?
I am not suggesting we should not worry about pollution – we should. But just because something is present does not automatically mean it is causing harm. To my mind, air pollution is the biggest worry so far, with more proven health effects than microplastics or PFAS.
Scary headlines generate clicks, views and likes but they rarely reflect the science.
We must understand relative exposure and the nuances of risk assessment. We need sensible debate, evidence-based approaches and new techniques for monitoring and assessing the impacts of, low (parts per trillion) pollutant concentrations.
This should help prevent and mitigate potentially harmful exposures in future.
![]()
Oliver A.H. Jones receives funding from the Australian Research Council, various water utilities, EPA Victoria and the Defence Science Institute for research into environmental pollution, including PFAS.
– ref. Environmental pollution and human health – how worried should we be? – https://theconversation.com/environmental-pollution-and-human-health-how-worried-should-we-be-233819




